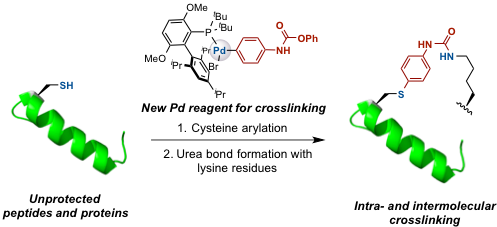
A new method for cysteine-lysine crosslinking in peptides and proteins using palladium oxidative addition complexes is presented. First, a biarylphosphine-supported palladium reagent is used to transfer an aryl group bearing an O-phenyl carbamate substituent to a cysteine residue. Next, this carbamate undergoes chemoselective acyl substitution by a proximal lysine to form a crosslink. The linkage so formed is stable towards acid, base, oxygen and external thiol nucleophiles. This method was applied to crosslink cysteine with nearby lysines in sortase A*. Furthermore, we used this method for the intermolecular crosslinking between a peptide and a protein based on the p53-MDM2 interaction. These studies demonstrate the potential for palladium-mediated methods to serve as a platform for the development of future crosslinking techniques for peptides and proteins with natural amino acid residues.A new method for cysteine-lysine crosslinking in peptides and proteins using palladium oxidative addition complexes is presented. First, a biarylphosphine-supported palladium reagent is used to transfer an aryl group bearing an O-phenyl carbamate substituent to a cysteine residue. Next, this carbamate undergoes chemoselective acyl substitution by a proximal lysine to form a crosslink. The linkage so formed is stable towards acid, base, oxygen and external thiol nucleophiles. This method was applied to crosslink cysteine with nearby lysines in sortase A*. Furthermore, we used this method for the intermolecular crosslinking between a peptide and a protein based on the p53-MDM2 interaction. These studies demonstrate the potential for palladium-mediated methods to serve as a platform for the development of future crosslinking techniques for peptides and proteins with natural amino acid residues.
